This is an old revision of the document!
Managing ROC-DNS
To get access to ROC-DNS, you must provision a ROC and then login to the Threat Detection dashboard. If you haven't done so yet, please check the guide on provisioning a ROC.
Our enterprise level ROC-DNS is based on state of the art threat detection to ensure that your endpoints are protected. It uses its threat algorithm analysis to block malicious or suspicious domains. It is made up of a combination of opensource and proprietary solutions.
Getting Started with DNS Management
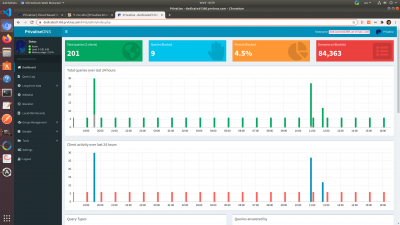
Once you login, you will see a quick overview of the DNS dashboard. Here you'll see the number of connected clients, queries blocked, and the number of the domains on the blocklist. You'll also see client and query activity over the last 24 hours.
Query Logging
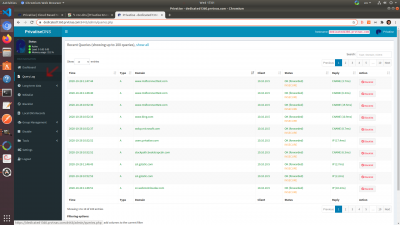
You will be able to see specific queries and break it down to the device level.
Some of your company clients might ask for query logging to be disabled for privacy reasons. You can do that under settings.
Allow & Disallow / Whitelisting & Blacklisting
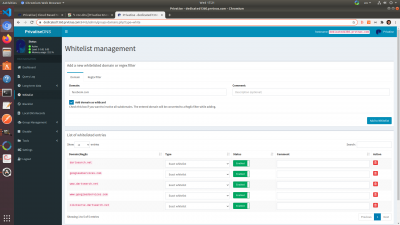
You can whitelist and blacklist domains directly from the dashboard. They work the same way, with the only difference being that whitelisting allows domains through the filter, and blacklist rejects domains through the filter.
Whitelisting is useful if you see in the Audit Log that a site was blocked that you don't want to block. Blacklisting is useful for banning specific websites for whatever reason.
You can whitelist or blacklist a domain by doing the following:
Under whitelisting or blacklisting, enter the domain you want to whitelist or blacklist. Make sure to add domain as wildcard
Then click the “Add to whitelist” or “Add to blacklist” button depending on which one you are doing.
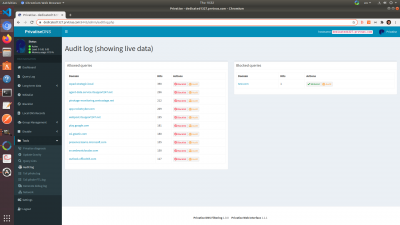
Audit Logs, Query Lists, Debugging
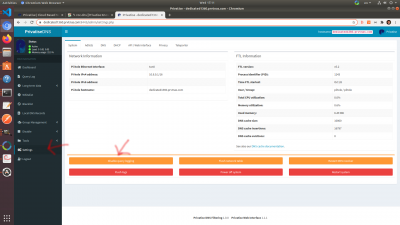
You will be able to create audit logs, query lists, and do debugging under “tools” menu item on the sidebar.
This is where you can see queries, audit blocked and permitted domains, and troubleshoot any issues.
DNS Filtering when using Active Directory on LAN
You can use Privatise DNS filtering in conjunction with your Active Directory on the local network. Please see our guide to Remote Access for more information.
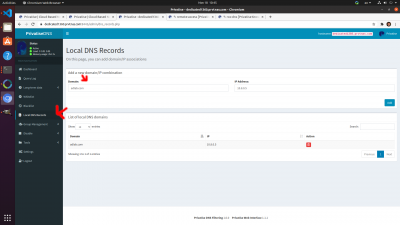
Custom Fully Qualified Domain Names
You can attach Fully Qualified Domain Names to an individual IP if it's static. To do so:
1. Go to Local DNS Records
2. Add a Fully Qualified Domain Name on the left, and static IP of the Privatise agent you want to connect to.
3. Alternatively, you can add an IP address of a general local domain, for example of an office router that is port forwarded to a server.